Page 22 - Delaware Medical Journal - February 2018
P. 22
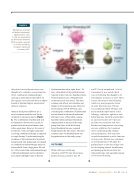
FIGURE 1
Mechanism of action of Opdivo (nivolumab) against tumor cells. T cells are inactivated by interaction between PD-1 receptors present on T cells and PD-L2 receptors expressed on tumor cells.7
the patient’s acute thyrotoxicosis was thought to be related to recent initiation of her combination immunotherapy causing an autoimmune thyroiditis. In this regard, corticosteroids have an added ��������������������������������������� immune response.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a
novel treatment modality used for the treatment of advanced cancers (Figure
1). The combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab has shown better results in patients with advanced melanoma than either agent alone. However, the rates of all adverse events are higher in patients receiving combination therapy as opposed to single therapy.4 Further analyzing the incidence of thyroid disorders in patients being treated with ipilimumab, nivolumab or combination immunotherapy based on data available from a large phase III trial (n= 945) revealed that combination therapy with both ipilimumab and nivolumab is associated with higher rates of thyroid
dysfunction than either agent alone.5 Of note, all incidents of thyroid dysfunction reported in this trial were hypothyroidism. No documented cases of hyperthyroid
or thyrotoxicosis were noted. The most common side effects were diarrhea and fatigue in all treatment groups. However, the Checkmate 067 & 069 trials, also evaluating the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab in advanced melanoma, did report cases of thyroiditis causing hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Approximately 8 percent of the study group from these trials did develop hyperthyroidism but none required hospitalization for this reason. The most common cause for hospitalization was hypopituitarism in this study group.6
OUTCOME
Within 48 hours of therapy initiation with PTU and intravenous hydrocortisone, patient’s free T4
and T3 levels normalized. A brief transaminitis was noted which
was self limiting but thought to be autoimmune in nature as well. There was no elevation of total bilirubin, which is a poor prognostic factor
in acute thyrotoxicosis. Patient
was extubated within 48 hours and had a marked improvement in her lethargy, confusion, agitation, and hallucinations. Initially, patient had an ejection fraction of 15 percent
and she was started on oral beta blockers and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors for treatment
of her cardiomyopathy. Repeat echocardiogram a few days later revealed normalized systolic function to 60 percent. Patient was continued on oral prednisone with plans for gradual taper as she was at high risk ������������������������������������� and panhypopituitarism from her immunotherapy and supraphysiologic corticosteroid dosing.
54
Del Med J | February 2018 | Vol. 90 | No. 2